Answer:
Ea = 177x10³ J/mol
ko =
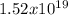 J/mol
J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The specific reaction rate can be calculated by Arrhenius equation:
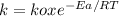
Where k0 is a constant, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T the temperature in Kelvin.
k depends on the temperature, so, we can divide the k of two different temperatures:
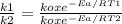
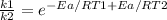
Applying natural logathim in both sides of the equations:
ln(k1/k2) = Ea/RT2 - Ea/RT1
ln(k1/k2) = (Ea/R)x(1/T2 - 1/T1)
R = 8.314 J/mol.K
ln(2.46/47.5) = (Ea/8.314)x(1/528 - 1/492)
ln(0.052) = (Ea/8.314)x(-1.38x
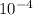
-1.67x
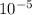 xEa = -2.95
xEa = -2.95
Ea = 177x10³ J/mol
To find ko, we just need to substitute Ea in one of the specific reaction rate equation:
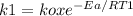
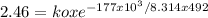
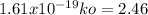
ko =
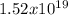 J/mol
J/mol