Answer:
100.223°C is the boiling point of an aqueous solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
Osmotic pressure of the solution = π = 10.50 atm
Temperature of the solution =T= 25 °C = 298 .15 K
Concentration of the solution = c
van'y Hoff factor = i = 1 (non electrolyte)
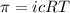
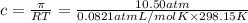
c = 0.429 mol/L = 0.429 mol/kg = m
(density of solution is the same as pure water)
m = molality of the solution
Elevation in boiling point =
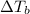
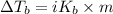
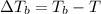
T = Boiling point of the pure solvent
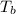 = boiling point of the solution
= boiling point of the solution
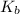 = Molal elevation constant
= Molal elevation constant
We have :
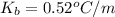 (given)
(given)
m = 0.429 mol/kg
T = 100° C (water)
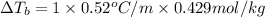
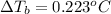
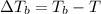
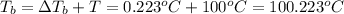
100.223°C is the boiling point of an aqueous solution.