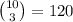Answer:
a)
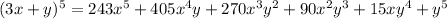 .
.
b) The middle term in the expansion is
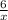 .
.
c) The coefficient of
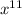 is 120.
is 120.
Explanation:
Remember that the binomial theorem say that
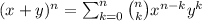
a)
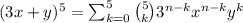
Expanding we have that
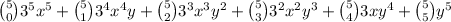
symplifying,
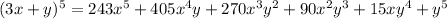 .
.
b) The middle term in the expansion of
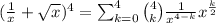 correspond to k=2. Then
correspond to k=2. Then
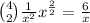 .
.
c)
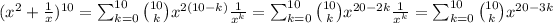
Since we need that 11=20-3k, then k=3.
Then the coefficient of
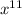 is
is