Answer:
0.5mL of the injection should be administered to obtain 0.02 g of the drug.
Explanation:
First step: The first step of this problem is the conversion of 0.02g to mg.
Each gram has 1000 miligrams. So:
1g - 1000mg
0.02g - xmg
x = 1000*0.02
x = 20mg
Final step:
A vial contains 80 mg of drug in 2 mL of injection. How many mL should be administered to obtain 0.02 g = 20mg of the drug.
This can be solved as a rule of three problem.
In a rule of three problem, the first step is identifying the measures and how they are related, if their relationship is direct of inverse.
When the relationship between the measures is direct, as the value of one measure increases, the value of the other measure is going to increase too.
When the relationship between the measures is inverse, as the value of one measure increases, the value of the other measure will decrease.
In this step, as the dose of the injection increases, so the quantity of the drug. So the relationship between the measures is direct. So:
80 mg - 2mL
20 mg - xmL
80x = 40
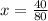
x = 0.5mL
0.5mL of the injection should be administered to obtain 0.02 g of the drug.