Answer:
D) 0.04
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming that a is the recessive allele when homozygous that causes the polycystic kidney disease and A is the dominant one:
Since Penelope's sisters has the disease, she must be homozygous recessive (aa). Her parents must both be Aa (otherwise her sister wouldn't have inherit the disease). So, the probability of Penelope of being heterozygous (Aa) is 0.5.
On the other hand, the probability of having the disease in the population is 0.04 (1 minus the probability of not having the disease which is 0.96). This, according the Hardy–Weinberg principle, in the population would represent the genotype frequency
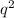 . So, the allele a would have a frequency
. So, the allele a would have a frequency
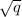 =
=
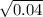 = 0.2. Since the gene has only two alleles, all alleles must be either A or a , therefore p + q = 1. So, the A population's frequency is p = 1 - q = 1 - 0.2 = 0.8.
= 0.2. Since the gene has only two alleles, all alleles must be either A or a , therefore p + q = 1. So, the A population's frequency is p = 1 - q = 1 - 0.2 = 0.8.
The European man's probability of being Aa (doesn't have the disease but can carry the disease allele) is 2pq = 2 x 0.8 x 0.2 = 0.32.
The probability of Penelope and the European man of having an ill kid (assuming they both are Aa) is 0.25.
Finally, given the Penelope's probability of being Aa (0.5), the European man's 's probability of being Aa (0.32) and the probability of having a kid homozygous recessive aa (0.25) = 0.5 x 0.32 x 0.25 = 0.4 is the probability that they will have a child with ARPKD.