Answer:
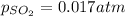
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
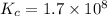
Relation of
 with
with
 is given by the formula:
is given by the formula:
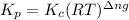
Where,
 = equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
= equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = ?
 = equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
= equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
R = Gas constant =
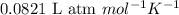
T = temperature =
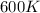
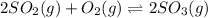
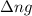 = change in number of moles of gas particles =
= change in number of moles of gas particles =
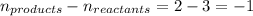
Putting values in above equation, we get:
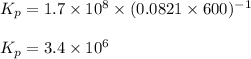
The chemical reaction follows the equation:
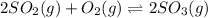
The expression for
 for the given reaction follows:
for the given reaction follows:
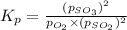
We are given:
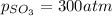
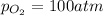
Putting values in above equation, we get:
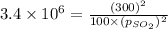
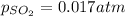
Hence, the partial pressure of the
 at equilibrium is 0.017 atm.
at equilibrium is 0.017 atm.