Answer:
4.1 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
Kinetic energy, K = 0.8 eV = 0.8 x 1.6 x 10^-19 J = 1.28 x 10^-19 J
wavelength, λ = 253.5 nm = 253.5 x 10^-9 m
According to the Einstein energy equation
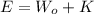
Where, E be the energy incident, Wo is the work function and K is the kinetic energy.
h = 6.634 x 10^-34 Js
c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
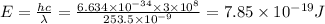
So, the work function, Wo = E - K
Wo = 7.85 x 10^-19 - 1.28 x 10^-19
Wo = 6.57 x 10^-19 J
Wo = 4.1 eV
Thus, the work function of the metal is 4.1 eV.