Answer:
![r=-3.73x10^(5)s^(-1) [CS_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9nwguduueucjbnqz3dct9mtmg15lm6qwnt.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, a linealization helps to choose the rate law for the decomposition of CS₂ as it is generalized via:
![r=-k[CS_2]^(n)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/56kmx4qix4plm3jp3nyhgiiif6sazk431g.png)
Whereas
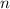 accounts for the order of reaction, which could be computed by linealizing the given data using the following procedure:
accounts for the order of reaction, which could be computed by linealizing the given data using the following procedure:
![-ln(r)=ln(k[CS_2]^(n))\\-ln(r)=ln(k)+ln([CS_2]^(n))\\-ln(r)=ln(k)+n*ln([CS_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dke4jsn06vfe43o0rxbl7j2y0jhaoczofs.png)
Therefore, on the attached picture you will find the graph and the lineal equation wherein the slope is the order of the reaction and the y-axis intercept the natural logarithm of the rate constant. In such a way, the order of reaction is 1 and the rate constant is:
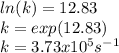
Best regards.