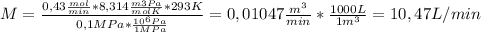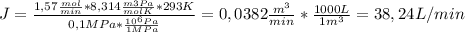Answer:
- Permeate stream: M=10,47 L/min
- Reject stream: J=38,24 L/min
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the law of mass conservation, we have that the moles of any component in the inlet air stream equals the moles of this compenent in the two outlets stream. Being A the mole flowrate for the permeate stream and B the mole flowrate for the reject stream (both in mol/min), we have equation (1) and (2):
2 mol/min * 0,21 = A mol/min * 0,50 + B mol/min * 0,13 ......................(1)
0,42 = 0,5A + 0,13B...........................(1)
2 mol/min * 0,79 = A mol/min * 0,50 + B mol/min * 0,87 ......................(2)
1,58 = 0,5A + 0,87B...........................(2)
Solving this system:
1,58 = 0,5A + 0,87B...........................(2)
0,42 = 0,5A + 0,13B...........................(1)
1,16 = 0A + 0,74B...............................(2) - (1)
1.16=0,74B
1,16/0,74=B
B=1,57 mol/min
And now replacing B in equation (1):
1,58 = 0,5A + 0,87*1,57
1,58-1,37=0,5A
0,21/0,5=A
A=0,43 mol/min
To calculate the volumetric flowrate of the permeate stream (M) and the reject stream (J), we just replace the given and calculate data into the ideal gas equation:
PV=nRT,.................... V = nRT/P