Answer: The rate will increase by a factor of 9.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
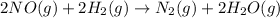
Given: Order with respect to
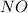 = 2
= 2
Order with respect to
 = 1
= 1
Thus rate law is:
![Rate=k[NO]^2[H_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/68o61fw1si3a3tk70fx1iqag4abx4ez5ak.png)
k= rate constant
It is given that the initial concentration of NO is tripled while all other factors stayed the same
![Rate'=k[3* NO]^2[H_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/y9lb63o28nfvqfhvhgs4xc0zthscrx25z0.png)
![Rate'=k[3]^2[NO]^2[H_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/50hzvjm95ho6p4y1rrdvgymlftqdjz1vno.png)
![Rate'=k* 9[NO]^2[H_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/v1limxdd6cku4ocpfh770azx9fi4qxiljf.png)
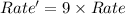
Thus the rate will increase by a factor of 9.