Answer:
Molar mass of unknown solute is 679 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume that the solute is a non-electrolyte.
For a solution with non-electrolyte solute remains dissolved in it -
Depression in freezing point of solution,
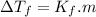
where, m is molality of solute in solution and
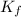 is cryogenoscopic constant of solvent.
is cryogenoscopic constant of solvent.
Here
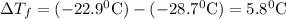
If molar mass of unknown solute is M g/mol then-
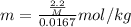
So,
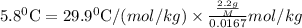
so, M = 679 g/mol