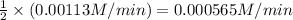Answer:
Average rate of reaction is 0.000565 M/min
Step-by-step explanation:
Applying law of mass action for the given reaction:
Average rate =
![-(1)/(2)([N_(2)O_(5)])/(\Delta t)=(1)/(4)(\Delta [NO_(2)])/(\Delta t)=(\Delta [O_(2)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5c9qps4x4quk3p11tjbbgu5aszmbtheb4n.png)
Where,
![-(1)/(2)([N_(2)O_(5)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/kdqklkobatlnmdl7kmgx4o8jk47traqg3m.png) represents average rate of disappearance of
represents average rate of disappearance of
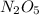 ,
,
![(1)/(4)([NO_(2)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7ac1m0fl02crjww41dassne1xnduzembo5.png) represents average rate of appearance of
represents average rate of appearance of
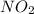 and
and
![([O_(2)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3gkru6ruzeiqirk191x8qpe55z78wm4da2.png) represents average rate of appearance of
represents average rate of appearance of
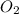
Here,
![-([N_(2)O_(5)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/g0d1thy61sjykexctqe8zg2vxl02ifezka.png) =
=
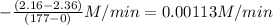
So average rate of reaction =
![[tex]-(1)/(2)([N_(2)O_(5)])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3r5u5l3lobvm4c886056y23puphg3ty2gr.png) [/tex] =
[/tex] =