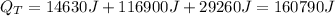Answer:
160790 J
Step-by-step explanation:
We can find the heat necessary for the ice to go from -20 degrees Celsius to 0 degrees Celsius:
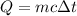
Where
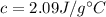 is the specific heat of ice, that is the amount of heat that must be supplied per unit mass to raise its temperature in a unit.
is the specific heat of ice, that is the amount of heat that must be supplied per unit mass to raise its temperature in a unit.
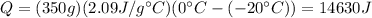
We must calculate the latent heat of fusion required for this ice mass to change to water:
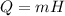
Where H=334 J/g is the specific latent heat of fusion of water, that is the amount of energy needed per unit mass of a substance at its melting point to change from the solid to the liquid state.
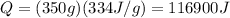
Then we calculate the heat necessary for the water to go from 0 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius:
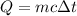
Where
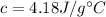 is the specific heat of water, that is the amount of heat that must be supplied per unit mass to raise its temperature in a unit.
is the specific heat of water, that is the amount of heat that must be supplied per unit mass to raise its temperature in a unit.
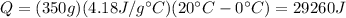
Finally the 3 results are added: