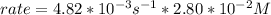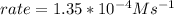Answer:
Part A
![rate= 4.82*10^(-3)s^(-1) * [N2O5]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1fynj8bb11hpb7upyv3swdhsg7ris8fd14.png)
Part B
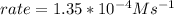
Step-by-step explanation:
Part A
The rate law is the equation that relates the rate of the reaction, the kinetic constant and the concentration of the reactant or reactants.
For the given chemical reaction we can write a general expression for the rate law as follows:
![rate= k * [N2O5]^(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ww8q2d52c0xgaknqsbqsl0my4ixmeue8bj.png)
where k is the rate constant and x is the order of the reaction with respect of N2O5 concentration. Particularly, a first order reaction kinetics indicate that the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of only one reactant. Then x must be 1.
Replacing the value of the rate constant given in the text we can arrive to the following expression for the rate law:
![rate= 4.82*10^(-3)s^(-1) * [N2O5]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1fynj8bb11hpb7upyv3swdhsg7ris8fd14.png)
Part B
Replacing the value of the concentration of N2O5 given, we can get the rate of reaction: