Answer: Option (A) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
pH = 7.40,
![[H_(2)CO_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4cb8h4wg5vwew8rndkm51ptjby94g4qsvn.png) =
=
![[CO_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/kbfvn81a84l7bcz4ysd6tqnt34djkqcfkv.png)
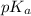 = 6.10
= 6.10
We have to find
![\frac{[HCO_^(-){3}]}{[CO_(2)]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9w5m2opo2k3w22ymb63hcdp9vf45szh2he.png) = ?
= ?
According to Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
pH =
![pK_(a) + log_(10) ([Salt])/([Acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zj01vlzrixbynpqu9lup2v79ckc2ik1q57.png)
Hence, putting the given values into the above equation as follows.
pH =
![pK_(a) + log_(10) ([Salt])/([Acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zj01vlzrixbynpqu9lup2v79ckc2ik1q57.png)
or, pH =
![pK_(a) + log_(10) ([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([H_(2)CO_(3)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/znw5o335jtcaepwfpp4gsv9725ncu71cxa.png)
7.40 = 6.10 +
![log_(10) ([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([H_(2)CO_(3)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2a3j2ifxyu9jho6f1aovvlytqbpn7k98jk.png)
![log_(10) ([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([H_(2)CO_(3)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2a3j2ifxyu9jho6f1aovvlytqbpn7k98jk.png) = 1.30
= 1.30
![([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([H_(2)CO_(3)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t9qufmlrjsi2hiwu0pg9zabjkrlj8ci95l.png) = antilog (1.30)
= antilog (1.30)
= 20
Since, it is given that
![[H_(2)CO_(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4cb8h4wg5vwew8rndkm51ptjby94g4qsvn.png) =
=
![[CO_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/kbfvn81a84l7bcz4ysd6tqnt34djkqcfkv.png) .
.
Therefore,
![([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([H_(2)CO_(3)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t9qufmlrjsi2hiwu0pg9zabjkrlj8ci95l.png) or
or
![([HCO^(-)_(3)])/([CO_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/haui76z3ew4wz9wcr09ntyttu66fd4took.png) =
=
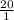
Thus, we can conclude that the bicarbonate (HCO3-) : carbon dioxide ratio for a normal blood pH of 7.40 is 20:1.