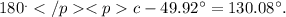Answer:
(a): 37.94 m.
(b):
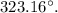
(c): 126.957 m.
(d):
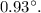
(e): 49.92 m.
(f):
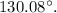
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
- Magnitude of
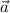 = 50 m.
= 50 m. - Direction of
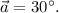
- Magnitude of
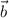 = 50 m.
= 50 m. - Direction of
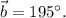
- Magnitude of
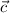 = 50 m.
= 50 m. - Direction of
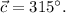
Any vector
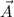 , making an angle
, making an angle
 with respect to the positive x-axis, can be written in terms of its x and y components as follows:
with respect to the positive x-axis, can be written in terms of its x and y components as follows:
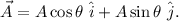
where,
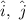 are the unit vectors along the x and y axes respectively.
are the unit vectors along the x and y axes respectively.
Therefore, the given vectors can be written as
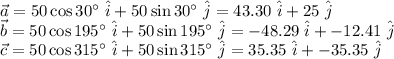
(a):
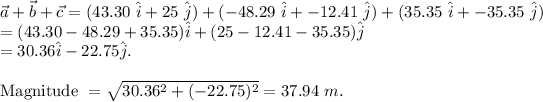
(b):
Direction
 can be found as follows:
can be found as follows:
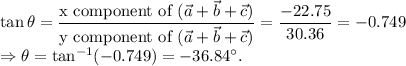
The negative sign indicates that the sum of the vectors is
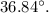 below the positive x axis.
below the positive x axis.
Therefore, direction of this vector sum counterclockwise with respect to positive x-axis =
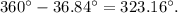
(c):
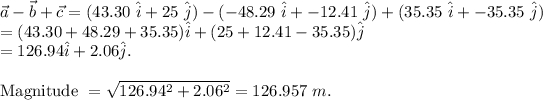
(d):
Direction
 can be found as follows:
can be found as follows:
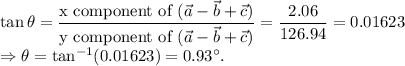
(e):
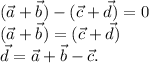
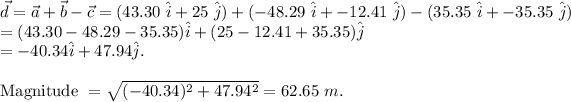
(f):
Direction
 can be found as follows:
can be found as follows:
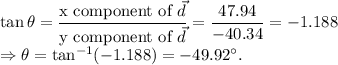
The x component of this vector is negative and y component is positive therefore the vector lie in second quadrant, which means, the direction of this vector, counterclockwise with respect to positive x axis =