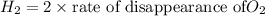Answer: Thus rate of disappearance of
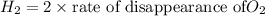
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
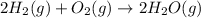
Given: Order with respect to
 = 2
= 2
Order with respect to
 = 1
= 1
Thus rate law is:
![Rate=k[H_2]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/16co83oknbs48cg8k9ipgbldm3ojjxxbww.png)
k= rate constant
The rate in terms of reactants is given as negative as the concentration of reactants is decreasing with time whereas the rate in terms of products is given as positive as the concentration of products is increasing with time.
![Rate=-(1d[H_2])/(2dt)=-(1d[O_2])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xih2rvt7xmxm7eyb49b7ubx0rfn419s9ka.png)
![Rate=-(1d[H_2])/(dt)=2* -(1d[O_2])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/a6uofh9iey15q1lq9qs3li1bdq67ndxsl5.png)
Thus rate of disappearance of