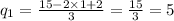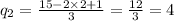Answer:
q1=5
q2=4
Step-by-step explanation:
In a Cournot model with a demand of the form
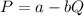 and firms with constant marginal costs we can easily find that the equilibrium quantities are given by
and firms with constant marginal costs we can easily find that the equilibrium quantities are given by
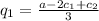
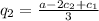
where
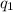 is the quantity produced by firm 1 and
is the quantity produced by firm 1 and
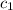 are its marginal costs. The same for firm 2.
are its marginal costs. The same for firm 2.
So replacing with the data given in the problem we have that