Answer:
Concentration of A at equilibrium = 1 - 0.5 = 0.5 M
Step-by-step explanation:
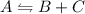
Equilibrium constant = 0.5
Initial concentration of A = 1 M
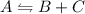
Initial 1 0 0
At equi. 1-x x x
Equilibrium constant =
![([B][C])/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bnlzm7qfshi7m2zmzwx36zgdbkr0tpiz2j.png)
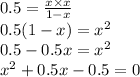
on solving,
x = 0.5 M
Concentration of A at equilibrium = 1 - 0.5 = 0.5 M