Answer:
460 mg drug is required for the patient whose weight is 23 kg .
Explanation:
It is given that a dose of a drug is 20 mg/kg.
It means for 1 kg weight 20 mg drug is required.
The ratio of drug and weight is
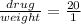
The weight of a patient = 23 kg
Let x mg drug is required for the patient whose weight is 23 kg. The ratio of drug and weight is
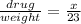
Equate both ratios.
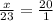
On cross multiplication we get
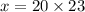
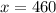
Therefore, 460 mg drug is required for the patient whose weight is 23 kg.