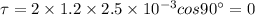Answer:
In first case
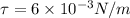 , In second case torque = 0
, In second case torque = 0
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given length of the square loop = 5 cm = 0.05 m
So area
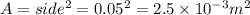
Current through the loop = 2 A
Magnetic field B = 1.2 T
We know that expression for flux
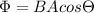
In first case there is maximum flux so
 must be zero
must be zero
So initial torque
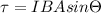 , here B is magnetic field, I is current and
, here B is magnetic field, I is current and
 is angle between magnetic field and area vector.
is angle between magnetic field and area vector.
So
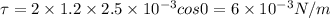
In second case flux is zero so
 must be 90°
must be 90°
So initial torque