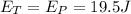Answer:19.5 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
mass of block=3 kg
angular frequency=20 rad/sec
spring constant
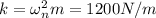
we know total energy remain conserved
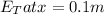
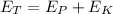
Where
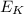 =kinetic energy
=kinetic energy
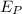 =potential Energy
=potential Energy
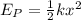

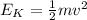
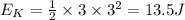
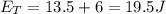
When mass reaches amplitude its velocity becomes zero
there is only potential energy which is equal to Total energy