Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
3 kg = 3 / 40 = .075 moles = n
a ) Since the gas is expanding isothermally ( temperature being constant )
work done by the gas
= 2.303 n RT log V₂ / V₁
Here V₂ / V₁ = 4 , T = 298
Put these values in the equation above ,
work done = .075x 2.303 x 8.312 x 298 log 4
= 257.6 J
b) In adibatic change
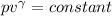
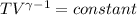
T₁ / T₂ =
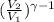
298 / T₂ =
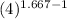
T₂ = 751.26 K.
In adiabatic change work done
= n R ( T₁ - T₂) / (γ -1)
.075x 8.312 X ( 751 - 298 ) / .667
= 423.38. J