Answer:
2.943 °C temperature change from the combustion of the glucose has been taken place.
Step-by-step explanation:
Heat released on combustion of Benzoic acid; :
Enthaply of combustion of benzoic acid = 3,228 kJ/mol
Mass of benzoic acid = 0.590 g
Moles of benzoic acid =
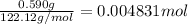
Energy released by 0.004831 moles of benzoic acid on combustion:
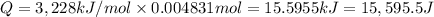
Heat capacity of the calorimeter = C
Change in temperature of the calorimeter = ΔT = 2.125°C
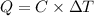
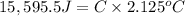
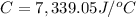
Heat released on combustion of Glucose: :
Enthaply of combustion of glucose= 2,780 kJ/mol.
Mass of glucose=1.400 g
Moles of glucose =
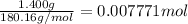
Energy released by the 0.007771 moles of calorimeter combustion:
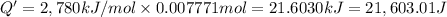
Heat capacity of the calorimeter = C (calculated above)
Change in temperature of the calorimeter on combustion of glucose = ΔT'
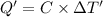
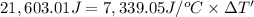
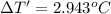
2.943 °C temperature change from the combustion of the glucose has been taken place.