Answer: -2.4 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
We can relate
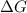 to
to
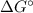 according to:
according to:
![\Delta G=\Delta G\°+RTln(([products]^n)/([reagents]^m))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7htd5pa6of3ostaagyjrvk9qowrab3c1nm.png)
Where [products] is the concentration of products, [reagents] is the concentrarion of reagents, n and m are the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients, T is the temperature in Kelvin and R is the gas constant.
Converting 37°C to Kelvin by adding 273, mM to M dividing by 1000, and substituting we get:
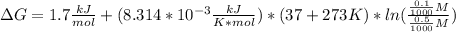
That gives us a value of -2.4 kJ/mol, the fouth option.