Answer:
Explanation has been given below.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider solubility equilibrium of an ionic insoluble compound e.g.
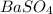
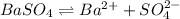
Equilibrium constant of this solubility equilibrium is represented in terms of solubility product (
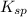 ) which is expressed as-
) which is expressed as-
![K_(sp)=[Ba^(2+)][SO_(4)^(2-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/eojmtmbkipv7xk5p0vd5tyqqx0mx01s29s.png)
Now, if we add an ionic salt e.g.
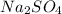 with a common ion
with a common ion
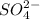 then concentration of
then concentration of
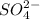 increases.
increases.
But, at a constant temperature,
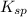 is constant.
is constant.
Therefore, to keep
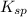 constant, excess amount of
constant, excess amount of
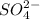 will combine with free
will combine with free
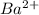 ion in solution and produce
ion in solution and produce
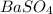 .
.
Hence, as a whole, solubility of
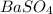 decreases.
decreases.