Answer:
The magnitude of the acceleration of the electron at this point is
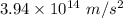 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Velocity
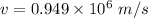
Angle = 61.5°
Magnetic field = 0.01 T
We need to calculate the magnetic force
Using formula of magnetic force
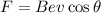
Where, B = magnetic field
v = velocity
e = charge of electron
Put the value into the formula
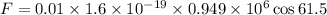

We need to calculate the acceleration
Using newton's second law
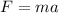
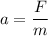
Put the value into the formula
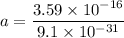
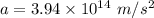
Hence, The magnitude of the acceleration of the electron at this point is
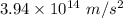 .
.