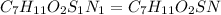Answer: The empirical formula for the given organic compound is
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the combustion of hydrocarbon having carbon, hydrogen and oxygen follows:
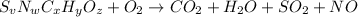
where, 'v', 'w' 'x', 'y' and 'z' are the subscripts of sulfur, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen respectively.
We are given:
Mass of
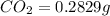
Mass of
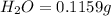
Mass of
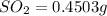
Mass of NO = 0.2109 g
We know that:
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44 g/mol
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Molar mass of sulfur dioxide = 64 g/mol
Molar mass of nitrogen monoxide = 30 g/mol
- For calculating the mass of carbon:
In 44 g of carbon dioxide, 12 g of carbon is contained.
So, in 2.1654 g of carbon dioxide,
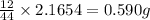 of carbon will be contained.
of carbon will be contained.
- For calculating the mass of hydrogen:
In 18 g of water, 2 g of hydrogen is contained.
So, in 0.6965 g of water,
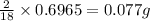 of hydrogen will be contained.
of hydrogen will be contained.
- For calculating the mass of sulfur:
In 64 g of sulfur dioxide, 32 g of sulfur is contained.
So, in 0.4503 g of sulfur dioxide,
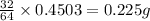 of sulfur will be contained.
of sulfur will be contained.
- For calculating the mass of nitrogen:
In 30 g of nitrogen monoxide, 14 g of nitrogen is contained.
So, in 0.2109 g of nitrogen monoxide,
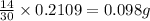 of nitrogen will be contained.
of nitrogen will be contained.
- Mass of oxygen in the compound = (1.2177) - (0.590 + 0.077 + 0.225 + 0.098) = 0.2277 g
To formulate the empirical formula, we need to follow some steps:
- Step 1: Converting the given masses into moles.
Moles of Carbon =
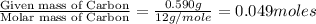
Moles of Hydrogen =
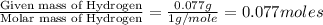
Moles of Oxygen =
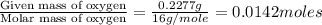
Moles of Sulfur =
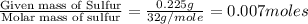
Moles of Nitrogen =
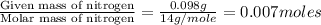
- Step 2: Calculating the mole ratio of the given elements.
For the mole ratio, we divide each value of the moles by the smallest number of moles calculated which is 0.007 moles.
For Carbon =
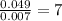
For Hydrogen =
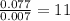
For Oxygen =
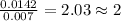
For Sulfur =
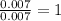
For Nitrogen =
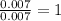
- Step 3: Taking the mole ratio as their subscripts.
The ratio of C : H : O : S : N = 7 : 11 : 2 : 1 : 1
Hence, the empirical formula for the given compound is