Step-by-step explanation:
We know that relation between
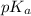 and
and
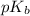 is as follows.
is as follows.
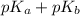 = 14
= 14
As it is given that
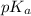 is 8.18. Therefore, calculate the value of
is 8.18. Therefore, calculate the value of
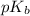 as follows.
as follows.
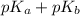 = 14
= 14
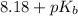 = 14
= 14
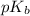 = 14 - 8.18
= 14 - 8.18
= 5.82
Similarly, as value of pH is given as 7.18. Therefore, value of pOH will be as follows.
pH + pOH = 14
7.18 + pOH = 14
pOH = 6.82
Let us take that B represents the enzyme. Hence, its reaction with proton will be as follows.
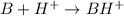 (protonated active enzyme)
(protonated active enzyme)
Hence, pOH =
![pK_(b) + log([BH^(+)])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/w3ce9cvs025lkeulo91g0c2oqifjnqe8xz.png)
6.82 = 5.82 +
![log_(10) ([BH^(+)])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/c6p0dnyy3nh4ewc56osznf26erk7st5goh.png)
![([BH^(+)])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/18ltgi9owgxel5l2silehet4jgb9joteop.png) = 10
= 10
Therefore, percentage of active enzyme = %
![[BH^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r7j7l6yynopem1wuu0qia9i8nk6cfauj4n.png) =
=
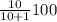
%
![[BH^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r7j7l6yynopem1wuu0qia9i8nk6cfauj4n.png) = 90.9%
= 90.9%
Thus, we can conclude that 90.9% is the percentage of the enzyme which is active in a buffer at pH 7.18.