Answer: a. The concentrations of the reactants and products have reached constant values
Step-by-step explanation:
The reactions which do not go on completion and in which the reactant forms product and the products goes back to the reactants simultaneously are known as equilibrium reactions. For a chemical equilibrium reaction, equilibrium state is achieved when the rate of forward reaction becomes equal to rate of the backward reaction.
Equilibrium state is the state when reactants and products are present but the concentrations does not change with time and are constant.
Equilibrium constant is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants each raised to the power their stoichiometric ratios. It is expressed as
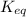
K is the constant of a certain reaction when it is in equilibrium, while Q is the quotient of activities of products and reactants at any stage other than equilibrium of a reaction.
For a equilibrium reaction,
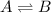
![K_(eq)=([B])/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/e8qwpx1xtgvw5on81kgowo8dhrjqbjsk4n.png)
Thus the correct answer is the concentrations of the reactants and products have reached constant values.