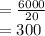Answer:
SA:V of the bacterium to that of the amoeba
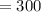
Step-by-step explanation:
Surface area (SA) of a sphere
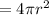
Volume (V) of a sphere
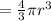
Surface area to volume ratio is equal to
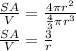
a) For bacteria of diameter
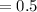 μm
μm
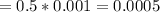 mm
mm
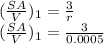
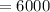
This means there is
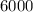 unit surface area per unit volume.
unit surface area per unit volume.
b) For amoeba with a diameter of
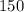 μm
μm
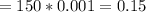 mm
mm
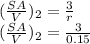
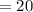
The ratio for SA:V of the bacterium to that of the amoeba