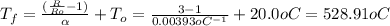Answer:
528.91°C
Step-by-step explanation:
Neglecting any change in dimensions, the way that the resistance of a material changes after a variation in its temperature is given by the expression:
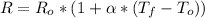
Where
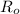 is the original resistance.
is the original resistance.
 is the temperature coefficient of the material, that relates the percentage that the resistance of the material will increase after a raise of 1°C in temperature. For copper, this value is equal to 0.00393/°C.
is the temperature coefficient of the material, that relates the percentage that the resistance of the material will increase after a raise of 1°C in temperature. For copper, this value is equal to 0.00393/°C.
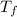 and
and
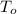 is the final and original temperature, respectively.
is the final and original temperature, respectively.