Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We will need a balanced chemical equation with masses and molar masses, volumes, and concentrations, so, let's gather all the information in one place.
M_r: 32.00
C₂H₅OH(l) + 3O₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) + 3H₂O(g)
m/g: 23.3
(a) Moles of O₂
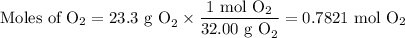
(b) Moles of CO₂
The molar ratio is 2 mol CO₂ = 3 mol O₂
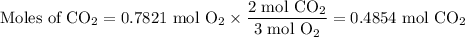
(c) Volume of CO₂
We can use the Ideal Gas Law to calculate the volume.
T = 25 °C = 298.15 K
