Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Second order decomposition (1 reactant) reaction means:
- rate = - d {HI] / dt = k [HI]² =
![\int\limits^([HI_1])_([HI_0]) {\,(d[HI])/([HI]^2)=-\int\limits^t_0 {t} \, dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/uh1dbox864b50vbvlp24576cf9bouuu8l0.png)
![(1)/([HI_t])-(1)/([HI_0])=kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/yzgy7qloumwj68stos97n4v93fzkxlu4wa.png)
When temperature and volume are kept constant concentration is proportional to pressure (P) and the rate may be expressed in terms of pressure as:
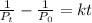
Here you have:
Therefore, substituting:
- 1 / 0.187atm - 1 / 0.691atm = 0.100 atm⁻¹ . min⁻¹ . t
- t = 3.900atm⁻¹ / 0.100 atm⁻¹ min⁻¹