Answer:
The molar concentration of Cu²⁺ in the initial solution is 6.964x10⁻⁴ M.
Step-by-step explanation:
The first step to solving this problem is calculating the number of moles of Cu(NO₃)₂ added to the solution:
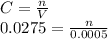
n = 1.375x10⁻⁵ mol
The second step is relating the number of moles to the signal. We know the the n calculated before is equivalent to a signal increase of 19.9 units (45.1-25.2):
1.375x10⁻⁵ mol _________ 19.9 units
x _________ 25.2 units
x = 1.741x10⁻⁵mol
Finally, we can calculate the Cu²⁺ concentration :
C = 1.741x10⁻⁵mol / 0.025 L
C = 6.964x10⁻⁴ M