Answer : The value of
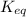 for the following reaction will be,
for the following reaction will be,

Explanation :
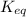 is defined as the equilibrium constant. It is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants.
is defined as the equilibrium constant. It is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants.
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
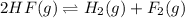
As we know that the concentrations of pure solids are constant that means they do not change. Thus, they are not included in the equilibrium expression.
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_(eq)=([H_2][F_2])/([HF]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/fdr5ui38vrt3fm7uwuxuj05hnbw98sl6ix.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
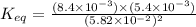
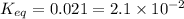
Therefore, the value of
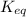 for the following reaction will be,
for the following reaction will be,
