Answer:
2.86 m
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
M₁ = 10 kg
M₂ = 5 kg
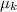 = 0.5
= 0.5
height, h = 5 m
distance traveled, s = 2 m
spring constant, k = 250 N/m
now,
the initial velocity of the first block as it approaches the second block
u₁ = √(2 × g × h)
or
u₁ = √(2 × 9.8 × 5)
or
u₁ = 9.89 m/s
let the velocity of second ball be v₂
now from the conservation of momentum, we have
M₁ × u₁ = M₂ × v₂
on substituting the values, we get
10 × 9.89 = 5 × v₂
or
v₂ = 19.79 m/s
now,
let the velocity of mass 2 when it reaches the spring be v₃
from the work energy theorem, we have
Work done by the friction force = change in kinetic energy of the mass 2
or
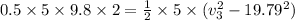
or
v₃ = 20.27 m/s
now, let the spring is compressed by the distance 'x'
therefore, from the conservation of energy
we have
Energy of the spring = Kinetic energy of the mass 2
or
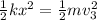
on substituting the values, we get
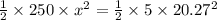
or
x = 2.86 m