Answer:
Theoretical yield of HI is 512 g.
The percent yield for this reaction is 25%.
Step-by-step explanation:
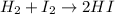
Moles of hydrogen gas = 3.0 moles
Moles of iodine gas = 2.0 moles
According to reaction 1 mol of hydrogen gas reacts with 1 mol of iodine gas.
Then 3.0 moles of hydrogen gas reacts with 3.0 mol of iodine gas. But there are 2.0 moles of iodine gas. Hence,Iodine is a limiting reagent. The production of HI will depend upon iodine gas moles.
According to reaction , 1 mol of iodine gas gives 2 moles of HI.
Then 2 moles of iodine gas will give:
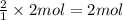 of HI
of HI
Theoretically we will get 4 moles of HI.
Theoretical yield of HI = 4 mol × 128 g/mol= 512 g
Experimental yield of HI = 1.0 mol
= 1 mol × 128 g/mol= 128 g
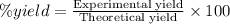
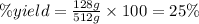
The percent yield for this reaction is 25%.