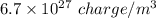Answer:
The density of charge carriers in the conductor is
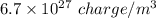
(d) is correct option.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Current = 2.0 A
Thickness = 0.50 mm
Hall voltage
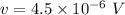
Magnetic field = 1.2 T
We need to calculate the density of charge carriers in the conductor
Using formula of the density of charge
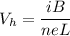
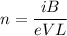
Where, i = current
B = magnetic filed
V = voltage
L = thickness
Put the value into the formula
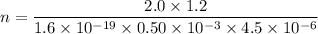
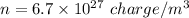
Hence, The density of charge carriers in the conductor is