Answer:
The equilibrium shifts towards reagents
Step-by-step explanation:
Is known
![Kc=([products])/([reagents])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hna2uquw22or5amd359vwhe22ia5bf75g6.png) rised to the power of their number of moles in the balanced reaction. When you have a system at equilibrium with Kc < 1, it means [products] < [reagents] and the system needs energy to react, so if you decrease tempeture the equilibrium shifts towards reagents and less products will be created.
rised to the power of their number of moles in the balanced reaction. When you have a system at equilibrium with Kc < 1, it means [products] < [reagents] and the system needs energy to react, so if you decrease tempeture the equilibrium shifts towards reagents and less products will be created.
This efect can be discribed with Van´t Hoff equation:
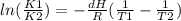 where we can see that if we decrease temperature (this is T2<T1) in consecuense K2<K1 and reaction doesn´t happen.
where we can see that if we decrease temperature (this is T2<T1) in consecuense K2<K1 and reaction doesn´t happen.