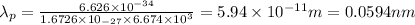Answer:
Given:
Thermal Kinetic Energy of an electron,
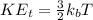
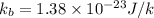 = Boltzmann's constant
= Boltzmann's constant
Temperature, T = 1800 K
Solution:
Now, to calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of the electron,
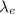 :
:
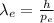
![\lambda_(e) = \frac{h}{m_(e){v_(e)}]() (1)
(1)
where
h = Planck's constant =
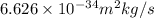
 = momentum of an electron
= momentum of an electron
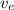 = velocity of an electron
= velocity of an electron
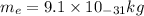 = mass of electon
= mass of electon
Now,
Kinetic energy of an electron = thermal kinetic energy
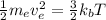
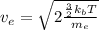
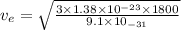
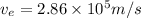 (2)
(2)
Using eqn (2) in (1):
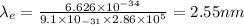
Now, to calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of proton,
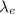 :
:
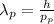
![\lambda_(p) = \frac{h}{m_(p){v_(p)}]() (3)
(3)
where
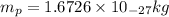 = mass of proton
= mass of proton
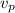 = velocity of an proton
= velocity of an proton
Now,
Kinetic energy of a proton = thermal kinetic energy
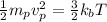
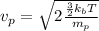
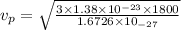
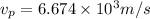 (4)
(4)
Using eqn (4) in (3):