Answer:
The correct answer is option b.
Step-by-step explanation:

The equation used to calculate Gibbs free change is of a reaction is:
![\Delta G^o_(rxn)=\sum [\Delta G^o_f(product)]-\sum [\Delta G^o_f(reactant)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9uz5uupzfqmkf3stq6v7fgylnzzh7k7lkq.png)
The equation for the enthalpy change of the above reaction is:

We are given:


Putting values in above equation, we get:

To calculate the
 (at 298 K) for given value of Gibbs free energy, we use the relation:
(at 298 K) for given value of Gibbs free energy, we use the relation:

where,
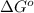 = Gibbs free energy = -35.2 kJ/mol = -35200 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1kJ = 1000J)
= Gibbs free energy = -35.2 kJ/mol = -35200 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1kJ = 1000J)
R = Gas constant =
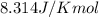
T =Temperature =298K[/tex]
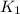 = equilibrium constant at 298 k;
= equilibrium constant at 298 k;
Putting values in above equation, we get:

Hence, correct answer is option b.