Step-by-step explanation:
(a) According to Le Chatelier's principle, any disturbance caused in an equilibrium reaction will shift the eqilibrium in a direction that will oppose the change.
For example,
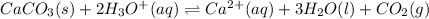
So, in this reaction when we any of the reactants then it means there is less stress on reactant side. Hence, the reaction will move in the backward direction.
Whereas when we remove
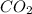 then there will be decrease in concentration of products as the concentration of carbon dioxide has decreased. Hence, the reaction will shift on the product side, that is, reaction will shift in the forward direction.
then there will be decrease in concentration of products as the concentration of carbon dioxide has decreased. Hence, the reaction will shift on the product side, that is, reaction will shift in the forward direction.
Thus, we can conclude that out of the given options removing
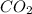 as it is formed would force the reaction to favor the produc to favor the products.
as it is formed would force the reaction to favor the produc to favor the products.
(b) As the reaction equation is as follows.
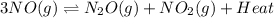
Since, it is an exothermic reaction, that means when temperature is increasing then more amount of energy will release on the product side.
Hence, the reaction will shift on the reactant side, that is on the left hand side equilibrium will shift.