Answer : The enthalpy change or heat required is, 139.28775 KJ
Solution :
The conversions involved in this process are :
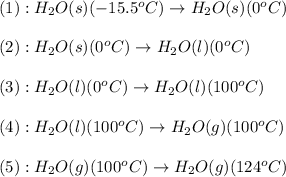
Now we have to calculate the enthalpy change.
![\Delta H=[m* c_(p,s)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+n* \Delta H_(fusion)+[m* c_(p,l)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+n* \Delta H_(vap)+[m* c_(p,g)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/n7h9q41ego6an5koia47cbt9qhwgwa66f3.png)
where,
 = enthalpy change or heat required = ?
= enthalpy change or heat required = ?
m = mass of water = 45 g
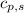 = specific heat of solid water =
= specific heat of solid water =
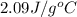
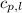 = specific heat of liquid water =
= specific heat of liquid water =
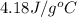
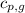 = specific heat of liquid water =
= specific heat of liquid water =
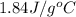
n = number of moles of water =
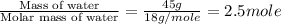
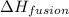 = enthalpy change for fusion = 6.01 KJ/mole = 6010 J/mole
= enthalpy change for fusion = 6.01 KJ/mole = 6010 J/mole
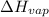 = enthalpy change for vaporization = 40.67 KJ/mole = 40670 J/mole
= enthalpy change for vaporization = 40.67 KJ/mole = 40670 J/mole
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get
![\Delta H=[45g* 4.18J/gK* (0-(-15.5))^oC]+2.5mole* 6010J/mole+[45g* 2.09J/gK* (100-0)^oC]+2.5mole* 40670J/mole+[45g* 1.84J/gK* (124-100)^oC]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ydma9g6gyan4atfpbdh1f68n9oymy7arhc.png)
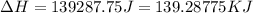 (1 KJ = 1000 J)
(1 KJ = 1000 J)
Therefore, the enthalpy change is, 139.28775 KJ