Answer:
The relative rates of diffusion for methane and oxygen is 1.4142.
Methane gas will be able to travel 1.4142 meter in the same conditions.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the rate of diffusion of gas, we use Graham's Law.
This law states that the rate of effusion or diffusion of gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of the gas. Mathematically written as:
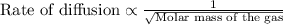
We are given:
Molar mass of methane gas, m = 16 g/mol
Molar mass of oxygen gas,m' = 32 g/mol
By taking their ratio, we get:
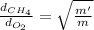
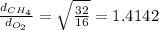
The relative rates of diffusion for methane and oxygen is 1.4142.
If oxygen gas travels 1 meters in time t.
Rate of diffusion of oxygen =
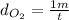
If methane gas travels travels in y meters in time t.
Rate of diffusion of methane=
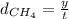
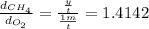
y = 1.4142 m
Methane gas will be able to travel 1.4142 meter in the same conditions.