Answer : The initial rate will be 0.2058 M/s
Explanation :
Rate law : It is defined as the expression which expresses the rate of the reaction in terms of molar concentration of the reactants with each term raised to the power their stoichiometric coefficient of that reactant in the balanced chemical equation.
The given reaction is,
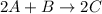
As we are given:
![Rate=0.4357[A][B]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/c83vyuw08bx03gbxkqalug2j1pjyour0la.png)
Initial concentration of A = 0.500 M
Initial concentration of B = 0.945 M
Now we have to calculate the initial rate.
![Rate=0.4357[A][B]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/c83vyuw08bx03gbxkqalug2j1pjyour0la.png)
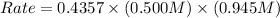
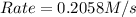
Therefore, the initial rate will be 0.2058 M/s