Answer: a) Anode:
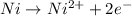
Cathode :
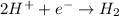
b)
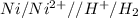
c) As
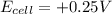 , the reaction is spontaneous.
, the reaction is spontaneous.
d)
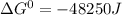
Step-by-step explanation:
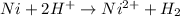
a) Here Ni undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. Hydrogen undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
Anode:
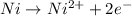
Cathode :
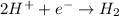
b) The representation is given by writing the anode on left hand side followed by its ion with its molar concentration. It is followed by a slat bridge. Then the cathodic ion with its molar concentration is written and then the cathode.
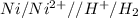
c)
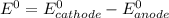
Where both
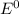 are standard reduction potentials.
are standard reduction potentials.
![E^0_([Ni^(2+)/Ni])= -0.25V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t5l3ohnjkm2lhzjkb99caguzpkrj4gxbfu.png)
![E^0_([H^(+)/H_2])=+0.0V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/an6zs5quvbaysfmjjuef7hjnnmsz7tjwnb.png)
![E^0=E^0_([H^(+)/H_2])- E^0_([Ni^(2+)/Ni])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vhonc9nyn27ggo6nhgw3c5tertpvqycdrh.png)
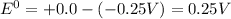
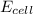 = +ve, reaction is spontaneous
= +ve, reaction is spontaneous
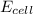 = -ve, reaction is non spontaneous
= -ve, reaction is non spontaneous
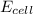 = 0, reaction is in equilibrium
= 0, reaction is in equilibrium
Thus as
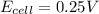 , the reaction is spontaneous.
, the reaction is spontaneous.
d) The standard emf of a cell is related to Gibbs free energy by following relation:
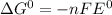
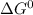 = standard gibbs free energy
= standard gibbs free energy
n= no of electrons gained or lost
F= faraday's constant
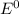 = standard emf
= standard emf
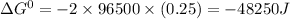
Thus value of Gibbs free energy is -48250 Joules.