Answer: Option (d) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
An oxidizing agent is defined as the substance that itself gains an electron and helps in oxidation of another substance.
For example,
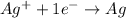
Here,
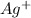 is the oxidizing agent.
is the oxidizing agent.
Also, a substance with more positive value of electrode potential will be the strongest oxidizing agent. Whereas a substance with more negative value of electrode potential will be the strongest reducing agent.
Therefore, out of the given options
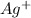 has the highest positive value of electrode potential so,
has the highest positive value of electrode potential so,
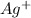 is the strongest oxidizing agent.
is the strongest oxidizing agent.