Answer:
(i) Calculate the average rate of consumption of A in the first 15 seconds of reaction: -8.67X10^(-3) M/s
(ii) Calculate the average rate of production of C in the first 15 seconds of reaction: 0.0.17 M/s
(iii) Calculate the average rate of consumption of A in the last 15 seconds of the reaction: -3x10^(-3) M/s
(iv) Explain the difference between the rates of consumption calculated in (i) and that in (iii): At the beginning the reaction, is fast, then, when time passes, the reaction slows because there are less concentration of the reactants to produce C, so the rate is less.
Step-by-step explanation:
The general formula to calculate any reaction rate is:
![r=(\Delta [Concentration])/(\Delta t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/60mxih10h4oeava9rkg19ogxmqrsie0usp.png)
With this formula we can make the calculations, and we can know if r is positive or negative by knowing if we are calculating for a reactant or a product, positive for products, negative for reactants.
(i)
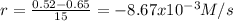
(ii)
In this case we need to multiply delta by 2, because 1 mole of A produces 2 moles of C:
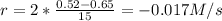
As we know it is a product, r needs to be positive, so we change the sign of the result and we have: 0.017 M/s
(iii)
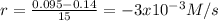
(iv)
Is already answered in the upper part.