Explanation :
Barfoed's test : Monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides can be distinguish by this test. The test solution is prepared by dissolving copper (II) acetate in acetic acid.
The equation for the oxidation of glucose by CuO is:
(1)
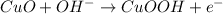
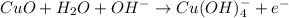
(2)
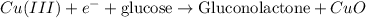
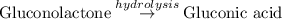
Here, CuO act as a catalyst.
In this reaction, first CuO salt get oxidized to form
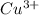 and then get reduced to back
and then get reduced to back
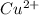 (CuO).
(CuO).
Hence, the equations are written above.